How Modal Analysis Prevents Vibration
Learn how modal analysis in FEA will help you avoid vibration in your production range.

Jon Thornham
Founder
Fan Vibration Correction
Industrial fans play a critical role in various applications, from ventilation systems to cooling processes and material handling. However, these essential machines can experience significant vibration issues, which can lead to mechanical failures, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance costs. Effective vibration mitigation strategies are vital to ensure the longevity and reliability of industrial fans. This article delves into the key aspects of fan vibration mitigation, including resonance of the fan wheel, in-situ balancing, vibration testing, and structural correction.

1.
Mechanical Imbalances: Uneven distribution of mass within the fan components leads to vibration, often due to manufacturing variations, wear over time, or improper assembly.2.
Misalignment: Incorrect alignment between the motor and fan shafts results in angular or parallel misalignment, causing vibrations during operation.3.
Bearing Failures: Defective or worn-out bearings due to insufficient lubrication, contamination, or normal wear introduce irregularities in rotational movements, leading to vibrations.4.
Aerodynamic Forces: Airflow dynamics and turbulence can induce vibrations in the fan blades and structure.5.
Resonance: Occurs when the natural frequency of the fan wheel matches the frequency of external excitations, leading to amplified vibrations.6.
Mechanical Looseness: Loose bolts, fasteners, or structural connections within the fan assembly can contribute to excessive movement and vibration.1.
Increased Wear and Tear: Vibrations accelerate wear on fan components, necessitating frequent repairs and replacements.2.
Operational Disruptions: Unplanned downtime due to vibration-related issues leads to production losses and scheduling disruptions.3.
Energy Inefficiency: Vibrations cause energy losses, affecting overall operational efficiency and increasing electricity costs.4.
Safety Concerns: Excessive vibrations pose safety risks to personnel and can compromise workplace safety standards.5.
Quality Control: Precision and accuracy in manufacturing processes may be compromised, leading to defective products and increased waste.The natural frequency of a fan wheel depends on its design, material, and operational conditions. Identifying this frequency is essential to avoid operating the fan at or near resonant frequencies. Methods to determine the natural frequency include:
1.
Modal Analysis: Study the vibrational modes of the fan wheel to identify its natural frequencies using finite element analysis (FEA) or experimental techniques such as impact testing.2.
Operational Deflection Shape (ODS) Analysis: Visualize how the fan wheel deforms at different frequencies during operation, providing insights into potential resonance issues.1.
Frequency Avoidance: Make design and operational adjustments to avoid running the fan at frequencies close to its natural frequency, such as changing the fan speed or modifying the system.2.
Damping: Increase damping within the system to reduce the amplitude of resonant vibrations using materials with higher damping properties or installing damping devices.3.
Stiffening the Structure: Increase the stiffness of the fan structure to raise its natural frequency, moving it away from the operating range by adding reinforcements or using stiffer materials.1.
Initial Vibration Measurement: Measure the vibration levels of the fan using accelerometers and vibration analyzers to identify the severity and location of the imbalance.2.
Balancing Calculations: Use the measured vibration data to calculate the amount and location of the required balancing weights.3.
Adding Balancing Weights: Attach balancing weights to the fan wheel at the calculated positions, ensuring they are securely fastened.4.
Verification: Remeasure the vibration levels after adding the weights to ensure that the imbalance has been corrected, making necessary adjustments.1.
Reduced Downtime: Allows for quick corrections without the need for disassembly, minimizing operational downtime.2.
Improved Accuracy: Balancing the fan in its operational position ensures all factors influencing vibration are considered, leading to more accurate results.3.
Cost-Effective: Often more cost-effective than removing and transporting the fan to an off-site balancing facility.Let us help you balance your fans and reduce vibration increasing bearing life.
1.
Operational Vibration Testing: Measure vibrations during normal operation to assess the current state of the fan and identify real-time issues.2.
Modal Testing: Excite the fan structure with controlled inputs and measure its response to determine natural frequencies and mode shapes.3.
Impact Testing: Strike the fan wheel with a calibrated hammer and measure the resulting vibrations to identify the dynamic characteristics of the system.1.
Baseline Measurement: Establish a baseline by measuring the current vibration levels of the fan under normal operating conditions.2.
Data Collection: Use accelerometers and other vibration sensors to collect data at various points on the fan and its components.3.
Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify the frequencies and amplitudes of vibrations, using spectral analysis to pinpoint specific sources.4.
Diagnosis and Mitigation: Diagnose the root causes of vibration issues and implement appropriate mitigation measures, such as balancing, alignment, or structural modifications.5.
Verification: Conduct another round of vibration testing after implementing mitigation measures to verify their effectiveness.1.
Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the fan and its supporting structure to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.2.
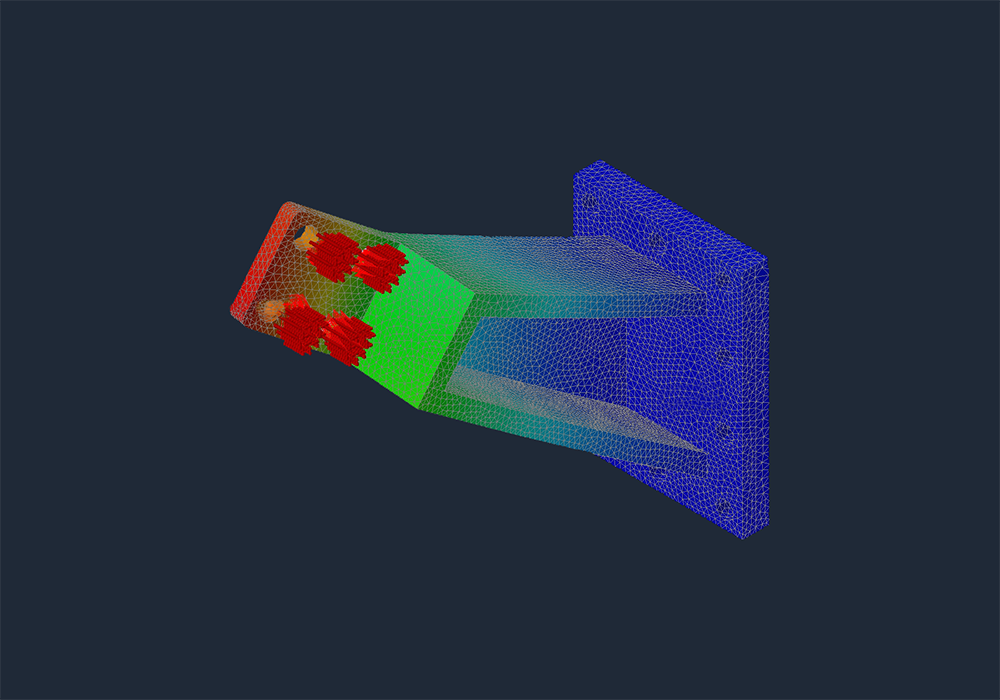
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Use FEA to simulate the stress and vibration response of the fan structure, identifying potential weak points and areas prone to resonance.1.
Reinforcing Weak Areas: Strengthen areas of the fan structure susceptible to excessive stress or vibration by adding braces, gussets, or using thicker materials.2.
Improving Support Systems: Ensure the fan is mounted on a stable and rigid foundation, using vibration isolation mounts or pads to reduce the transmission of vibrations.3.
Modifying Design: If structural issues persist, consider redesigning the fan or its supporting structure to improve stability and reduce vibrations.4.
Regular Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to check for signs of structural degradation and address issues promptly.Effective vibration mitigation is crucial for the reliable and efficient operation of industrial fans. By addressing resonance, ensuring proper in-situ balancing, conducting comprehensive vibration testing, and implementing structural corrections, industrial facilities can significantly reduce the risk of mechanical failures, enhance operational efficiency, and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Investing in vibration analysis and mitigation ensures smooth and efficient fan operations, contributing to overall safety and cost savings. Through meticulous planning, regular maintenance, and continuous monitoring, the challenges associated with fan vibrations can be effectively managed, ensuring the long-term success of industrial operations.
If you are seeing vibration issues on motors, fans, piping, turbines, or structural systems, this article covers only one piece of the diagnostic process. Our comprehensive Vibration Analysis and Engineered Correction guide shows how we use modal testing, ODS, FRFs, FEA, and field measurements to identify root causes and engineer permanent fixes.

Learn how modal analysis in FEA will help you avoid vibration in your production range.

Jon Thornham
Founder

Author Details
Founder
Jon Thornham is the founder of Vibration Engineers, a professional mechanical engineer, and entrepreneur focused on solving complex vibration and reliability challenges across industrial sectors.